Much of Wall Street expects easing inflation, but an overshoot could dash hopes of a May rate cut, curtailing the S&P 500’s
SPX
waltz with 5,000, warn some.
Read: Arm’s frenzied stock rally continues as AI chase trumps valuation.
What might take this market down eventually? Our call of the day from former hedge-fund manager Russell Clark points to Japan, an island nation whose central bank is one of the last holdouts of loose monetary policy.
Note, Clark bailed on his perma bear RC Global Fund back in 2021 after wrongly betting against stocks for much of a decade. But he’s got a whole theory on why Japan matters so much.
In his substack post, Clark argues that the real bear-market trigger will come when the Bank of Japan ends quantitative easing. For starters, he argues we’re in a “pro-labor world” where a few things should be playing out: higher wages and lower jobless levels and interest rates higher than expected. Lining up with his expectations, real assets started to surge in late 2023 when the Fed started to go dovish, and the yield curve began to steepen.
From that point, not everything has been matching up so easily. He thought higher short-term rates would siphon off money from speculative assets, but then money flowed into cryptos like Tether and the Nasdaq recovered completely from a 2022 rout.
“I have been toying with the idea that semiconductors are a the new oil – and hence have become a strategic asset. This explains the surge in the Nasdaq and the Nikkei to a degree, but does not really explain tether or bitcoin very well,” he said.
So back to Japan and his not so popular explanation for why financial/speculative assets continue to trade so well.
“The Fed had high interest rates all through the 1990s, and dot-com bubble developed anyway. But during that time, the Bank of Japan only finally raised interest rates in 1999 and then the bubble burst,” he said.
He notes that when Japan began to tighten rates in late 2006, “everything started to unwind,” adding that the BOJ’s brief attempts [to] raise rates in 1996 could be blamed for the Asian Financial Crisis.
In Clark’s view, markets seem to have moved more with the Japan’s bank balance sheet than the Fed’s. The BOJ “invented” quantitative easing in the early 2000s, and the subprime crisis started not long after it removed that liquidity from the market in 2006, he notes.
“For really old investors, loose Japanese monetary policy also explained the bubble economy of the 1980s. BOJ Balance Sheet and S&P 500 have decent correlation in my book,” he said, offering the below chart:
Capital Flows and Asset Markets, Russell Clark.
Clark says that also helps explains why higher bond yields haven’t really hurt assets. “As JGB 10 yields have risen, the BOJ has committed to unlimited purchases to keep it below 1%,” he notes.
The two big takeaways here? “BOJ is the only central bank that matters…and that we need to get bearish the U.S. when the BOJ raises interest rates. Given the moves in bond markets and food inflation, this is a matter of time,” said Clark who says in light of his plans for a new fund, “a bear market would be extremely useful for me.” He’s watching the BOJ closely.
The markets
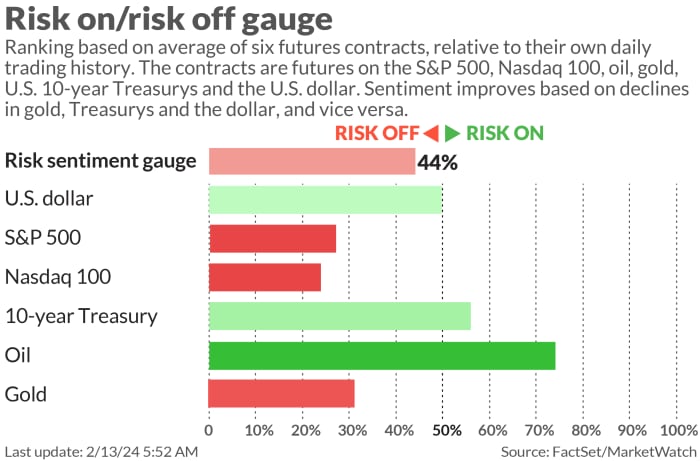
Pre-data, stock futures
ES00,
NQ00,
are down, while Treasury yields
BX:TMUBMUSD10Y
BX:TMUBMUSD02Y
hold steady. Oil
CL.1,
and gold
GC00,
are both higher. The Nikkei 225 index
JP:NIK
tapped 38,000 for the first time since 1990.
| Key asset performance | Last | 5d | 1m | YTD | 1y |
| S&P 500 | 5,021.84 | 1.60% | 4.98% | 5.28% | 21.38% |
| Nasdaq Composite | 15,942.55 | 2.21% | 6.48% | 6.20% | 34.06% |
| 10 year Treasury | 4.181 | 7.83 | 11.45 | 30.03 | 42.81 |
| Gold | 2,038.10 | -0.17% | -0.75% | -1.63% | 9.33% |
| Oil | 77.14 | 5.96% | 6.02% | 8.15% | -2.55% |
| Data: MarketWatch. Treasury yields change expressed in basis points | |||||
The buzz
Due at 8:30 a.m., January headline consumer prices are expected to dip to 2.9% for January, down from 3.4% in December and the lowest since March 2021. Monthly inflation is seen at 0.3%.
Biogen
BIIB,
stock is down on disappointing results and a slow launch for its Alzheimer’s treatment. A miss is also hitting Krispy Kreme
DNUT,
Coca-Cola
KO,
is up on a revenue rise, with Hasbro
HAS,
Molson Coors
TAP,
and Marriott
MAR,
still to come, followed by Airbnb
ABNB,
Akamai
AKAM,
and MGM Resorts
MGM,
after the close. Hasbro stock is plunging on an earnings miss.
JetBlue
JBLU,
is surging after billionaire activist investor Carl Icahn disclosed a near 10% stake and said his firm is discussing possible board representation.
Tripadvisor stock
TRIP,
is up 10% after the travel-services platform said it was considering a possible sale.
In a first, Russia put Estonia’s prime minister on a “wanted” list. Meanwhile, the U.S. Senate approved aid for Ukraine, Israel and Taiwan.
Best of the web
Why chocolate lovers will pay more this Valentine’s Day than they have in years
A startup wants to harvest lithium from America’s biggest saltwater lake.
Online gambling transactions hit nearly 15,000 per second during the Super Bowl.
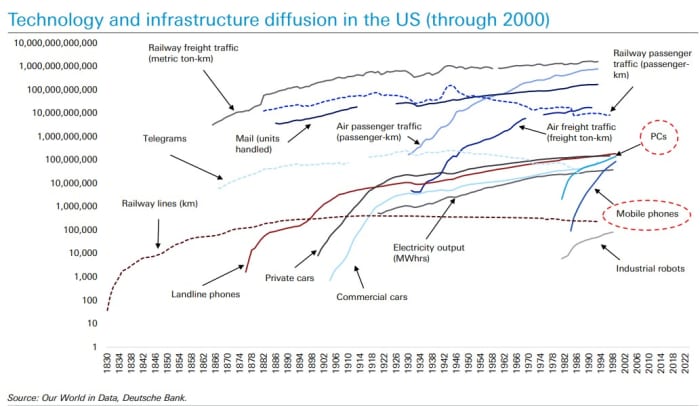
The chart
Deutsche Bank has taken a deep dive into the might of the Magnificent Seven, and why they will continue to matter for investors. One reason? Nearly 40% of the world still doesn’t have internet access as the bank’s chart shows:
Top tickers
These were the top-searched tickers on MarketWatch as of 6 a.m.
| Ticker | Security name |
|
TSLA, |
Tesla |
|
NVDA, |
Nvidia |
|
ARM, |
Arm Holdings |
|
PLTR, |
Palantir Technologies |
|
NIO, |
Nio |
|
AMC, |
AMC Entertainment |
|
AAPL, |
Apple |
|
AMZN, |
Amazon.com |
|
MARA, |
Marathon Digital |
|
TSM, |
NIO |
Random reads
Everyone wants this freak “It bag.”
Dumped over a text? Get your free dumplings.
Messi the dog steals Oscars’ limelight.
Love and millions of flowers stop in Miami.
Need to Know starts early and is updated until the opening bell, but sign up here to get it delivered once to your email box. The emailed version will be sent out at about 7:30 a.m. Eastern.
Check out On Watch by MarketWatch, a weekly podcast about the financial news we’re all watching – and how that’s affecting the economy and your wallet.
Source link
#hedge #fund #star #trigger #bear #market











