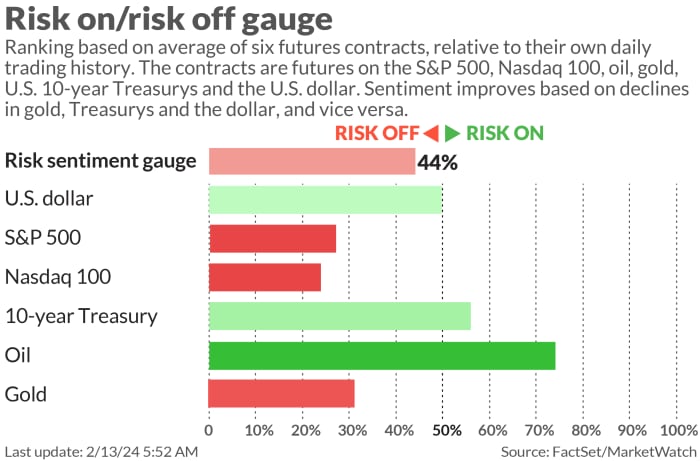
A four-month-long U.S. stock market rally, partly fueled by investors’ expectations for interest rate cuts in 2024 by the Federal Reserve, faces a test posed by pair of big events in the week ahead.
The first is Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell’s semiannual testimony to Congress on Wednesday and Thursday, followed by Friday’s official jobs report for February.
Of the two, the nonfarm payrolls data has the potential to move markets more, given what it could signal about the risk that inflation may keep running hot if job gains come in above the 190,000 consensus expectation, according to analysts and investors.
“Inflation has bottomed out, but is still above the Fed’s objective and it seems like more labor-market weakness is going to be needed,” said John Luke Tyner, a portfolio manager at Alabama-based Aptus Capital Advisors, which manages $5.5 billion in assets. “The headlines we’ve been seeing on technology-related layoffs are missing the mark because there’s a resurgence of employment and wage growth in Middle America.”
January’s data proves the point. The month of February began with the release of January nonfarm payrolls, which showed 353,000 jobs created and a sharp 0.6% rise in average hourly earnings for all employees, despite the highest interest rates in more than two decades.
Then came a round of inflation data. Consumer- and producer-price readings were both above expectations for January, followed by last Thursday’s release of the Fed’s preferred inflation measure, known as the PCE, which showed the monthly pace of underlying price gains rising at the fastest pace in almost a year. Meanwhile, personal income grew at a monthly rate of 1% in January.
Fed-funds futures traders have since pared back their expectations for as many as six or seven quarter-percentage point rate cuts by December, and moved closer in line with the three reductions that the Fed signaled would likely be appropriate. However, this has still been enough to hand the Dow Jones Industrial Average
DJIA
and S&P 500
SPX
their best start to a year since 2019, and fueled a four-month rally in all three major indexes. For the week, the S&P 500 rose 1% and the Nasdaq Composite gained 1.7%, but the Dow Jones slipped 0.1%, based on FactSet data.
Broadly speaking, Powell is expected to stick to his script by emphasizing the need for greater confidence that inflation is falling toward the Fed’s 2% objective, before policymakers can cut the fed-funds rate target from its current range of 5.25% to 5.5%, analysts said. He’s seen as loath to say anything just yet that could move markets or rate expectations.
“Powell needs to avoid doing what he did in November and December, which was to juice the market with a very bullish message suggesting that policymakers might be done with hiking rates and that the next moves would be rate cuts,” Tyner said via phone. “The Fed needs to remain unified about the need to be patient, with no rush to cut rates, and about being data dependent, with the current data pointing toward not cutting until later this year.”
Read: No Fed rate cuts in 2024, Wall Street economist warns investors
Aptus Capital’s strategies rely on the use of options overlays to improve results, and the firm is “well-positioned” to capture both upside and downside moves in the market because of a “disciplined approach on hedges in both directions,” the portfolio manager said.
Others see some possibility that Powell’s testimony to the House Financial Services Committee and Senate Banking Committee produces one of two non-base-case results: He could either push back on expectations around the timing or extent of Fed rate cuts this year, or, on the flip side, hint at the need for maintenance rate cuts because of prospects for softer inflation and economic readings going forward.
The rates market is the mechanism by which financial markets would likely react one way or another to Powell’s testimony and Friday’s nonfarm payrolls report — specifically with trading in fed-funds futures and Secured Overnight Financing Rate futures. Any reaction in the futures market would simultaneously impact longer-term Treasurys and risk assets, according to Mike Sanders, head of fixed income at Wisconsin-based Madison Investments, which manages $23 billion in assets.
Fed officials are not likely to have enough confidence that they’ve won the battle against inflation by June, raising the question of whether markets are overestimating policymakers’ ability to start cutting rates by that month, Sanders said via phone.
“Fed officials are more or less committed to cutting rates when appropriate, but are concerned that if they cut too soon they’ll have sticky inflation,” he said.
“The services side continues to be higher than the Fed wants, with much of the disinflation coming from the goods side,” Sanders said. Inflation dynamics are “still not in balance from the Fed’s perspective, and the services side has to be concerning to policymakers, especially in the face of the personal-income growth we’ve seen. It’s going to be status quo until the Fed knows whether the higher inflation prints seen in January were a one-off or if this continues.’’
Analysts said they are particularly worried about supercore inflation, a measure of core services that excludes housing, which is still running at levels which suggest that the services side of the U.S. economy is firing on all cylinders.
No major U.S. data is scheduled for release on Monday. Tuesday brings January factory orders and ISM service sector activity figures for February.
On Wednesday, data releases include ADP’s private-sector employment report, January readings on wholesale inventories and job openings, and the Fed’s Beige Book report. San Francisco Fed President Mary Daly is also set to speak that day.
Thursday’s data batch includes weekly initial jobless benefit claims, a revision on fourth-quarter productivity, the U.S. trade balance, and consumer-credit figures. Cleveland Fed President Loretta Mester is also scheduled to make an appearance. Friday brings an appearance by New York Fed President John Williams and final consumer-sentiment data for February.
Source link
#Stock #rally #ratecut #forecasts #face #test #Powell #testimony #jobs #report