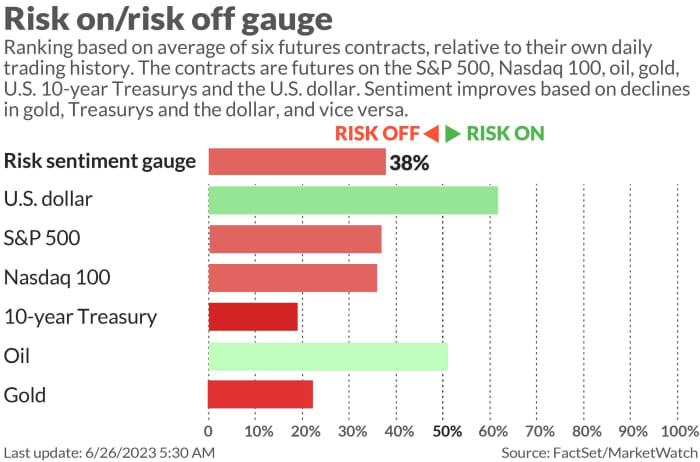
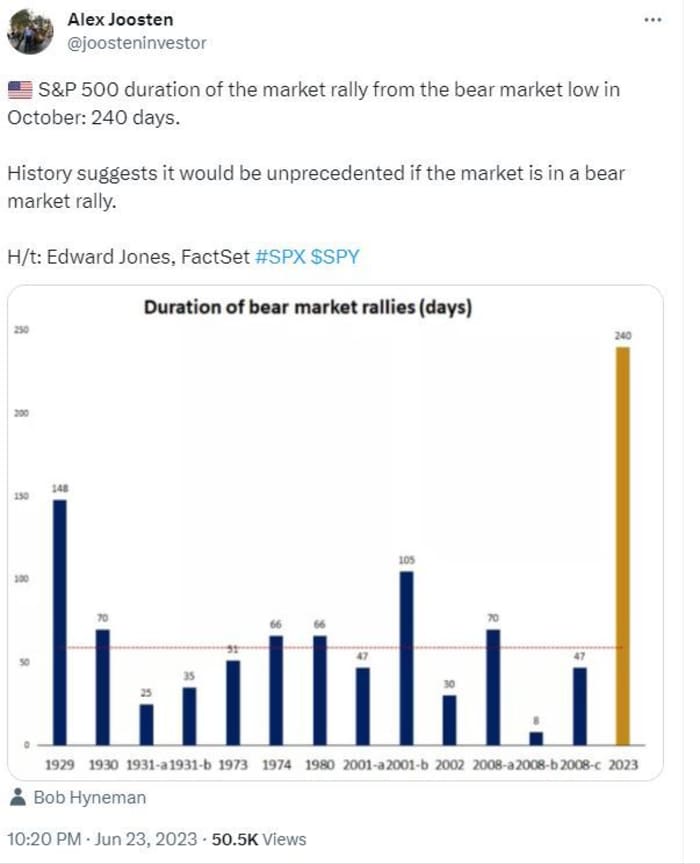
There’s always a bull market somewhere — if you can find it.
Keith McCullough encourages investors to join him in the hunt. You’ll need to be agnostic and open-minded, the CEO of investment service Hedgeye Risk Management says. If you’re wedded just to U.S. stocks, or the market’s latest darlings, you’re setting yourself up for disappointment — particularly in the hostile environment McCullough sees coming.
This coming challenge for U.S. stock investors, in a word, is stagflation, McCullough says. Stagflation — higher inflation plus slow- or no economic growth — is hardly a bullish outlook for stocks, but McCullough’s investment process looks for opportunties wherever they may be. Right now that’s led him to put money into health care, gold, Japan, India, Brazil and energy stocks, among others.
In this recent interview, which has been edited for length and clarity, McCullough takes the Federal Reserve and Chair Jerome Powell to the woodshed, offers a warning about the potential fallout from Powell’s upcoming speech at Jackson Hole, Wyo., and implores investors to discount happy talk and always watch what they do, not what they say.
MarketWatch: When we spoke in late May, you criticized the Federal Reserve for being obtuse and myopic in its response to inflation and, later, to the threat of recession. Has the Fed done anything since to give you more confidence?
McCullough: The Fed forecast of the probability of recession should be trusted as much as their “transitory” inflation forecast or a parlor game. People should not have confidence in the Fed’s forecast. The “no-landing” or “soft-landing” thesis is looking backwards. The Fed is grossly underestimating the future, doing what they always do, in looking at the recent past.
Their policy is wed to what they say. They claim they’re not going to cut interest rates until they get to their target. But any hint of the Fed arresting the tightening gives you more inflation. So there’s this perverse relationship where the Fed is the catalyst to bring back the inflation they’ve spent so much time fighting.
MarketWatch: U.S. Inflation has come down quite signficantly over the past year. Doesn’t that show the Fed is well on the way to achieving its 2% target?
McCullough: A lot of people are peacocking and declaring victory over inflation when we’re about to have reflation that sticks. We have inflation heading back towards 3.5% and staying there.
Our inflation forecast is that it’s set to reaccelerate in the next two inflation reports, which will lead to another rate hike in September. The Fed’s view is that until they get to the 2% target they’re not done. A lot of people are really confident because inflation went from 9% to 3% that it’s getting closer to 2%, therefore the Fed is done. Given what Fed Chair Jerome Powell said, the next two inflation reports are critical in determining whether we hike rates in September. I think maybe even one in November. This is a major catalyst for the next leg down in the equity market.
The Fed is going to see inflation go higher, and they’ve already articulated to Wall Street that no matter what happens, that should constitute a rate hike. That’s a policy mistake. They’re going to continue to tighten into a slowdown. When the Fed tightens into a slowdown, things blow up.
MarketWatch: By “things blow up,” you mean the stock market.
McCullough: I don’t think the Fed cuts interest rates until the stock market crashes. The Fed is going to be tightening when the U.S. economy and corporate profits are at a low point, going into the fourth quarter. It’s not dissimilar from 1987 where all of a sudden a market that looked fine got annihilated in very short order. There are a lot of similarities to 1987 now; the market’s quick start in January, people in love with stocks. That’s a catalyst for the stock market to crash.
When the Fed has an inconvenient rule, particularly for the U.S. stock market, they just move the goal posts or change the rule. If they actually started to cut interest rates, inflation would go up faster. This is exactly what happened in the 1970s and what Powell explains is the risk of going dovish too soon – that he becomes [much-criticized former Fed chair] Arthur Burns. That’s why you had rolling recessions in the 1970s; the Fed would go dovish, devalue the U.S. dollar
DX00,
and the cost of living for Americans would reflate to levels that are prohibitive.
People can’t afford reflation at the gas pump, or in their health care. It’ll be fascinating to see how Powell pivots from fighting for the people to bailing out Wall Street from another stock market crash, which will therein create the next reflation.
“ ‘The Federal Reserve has set the table for a major event in the U.S. stock market and the credit market.’”
MarketWatch: Speaking of a Powell pivot, the Fed chair speaks at Jackson Hole this week. Last year he put markets on notice for rate hikes. What do you think he’ll say this time?
Powell’s going to see inflation accelerating. I think Jackson Hole is going to be a hawkish meeting. That might be the trigger for the stock market.
Take the bond market’s word for it. The bond market is saying the Fed is going to remain tight and seriously consider another rate hike in September. The reasons why markets crash in October during recession is that the fourth quarter is when companies realize that there’s no soft landing and they need to guide down.
The Federal Reserve has set the table for a major event in the U.S. stock market and the credit market. We’re short high-yield and junk bonds through two ETFs: iShares iBoxx $ High Yield Corporate Bond
HYG
and SPDR Bloomberg High Yield Bond
JNK.
On the equity side the best thing is to short the cyclicals; I would short the Russell 2000
RUT.
MarketWatch: What’s your advice to stock investors right now about how to reposition their portfolios?
McCullough: Own what the “Mother of All Bubbles” crowd doesn’t. The things we’re most bullish on include gold
GC00,
The Fed is going to keep short term rates high and both the 10 year and 30 year go lower. Gold trades with real interest rates. I think gold can go a lot higher, towards 2,150. Our ETF for gold is SPDR Gold Shares
GLD.
Also, you can be long equities and not take on the heart-attack risk that is the U.S. stock market. I’m long Japanese equities — ETFs for this include iShares MSCI Japan
EWJ
and iShares MSCI Japan Small-Cap
SCJ.
We’re long India with iShares MSCI India
INDA
and iShares MSCI India Small-Cap
SMIN.
Both Japan and India are accelerating economically. Were also long Brazil iShares MSCI Brazil
EWZ,
which is weighted to energy. We are bullish on energy.
MarketWatch: Clearly accelerating inflation and slowing economic growth is an unhealthy combination for both investors and consumers.
McCullough: What I’m looking for, with inflation reaccelerating, is stagflation.
Stagflation pays the rich and punishes the poor. You want to be the landlord. The prices of things people own are going to go up, and the prices of things you need to live are also going to go up. So for example, we are long energy, uranium and timber as stagflation plays. ETFs we’re using for that include Energy Select Sector SPDR
XLE,
Global X Uranium
URA,
and iShares Global Timber & Forestry
WOOD.
One positive thing that happens from stagflation is that because it’s so hard to find real consumption growth, there’s a premium on the growth you can find.
If there is something that actually accelerates, then those stocks will work, which puts a nice premium on stock picking. You can be long anything that is accelerating because so many things are decelerating. So avoid U.S. consumer, retailers, industrials and financials, which are all decelerating. Health care is our favorite sector, which we own through the ETFs Simplify Health Care
PINK
and SPDR S&P Health Care Equipment
XHE.
Instead, people are betting we’re going to go back to some crazy AI-led growth environment. Now everyone thinks everything is AI and rainbows and puppy dogs. I’m old enough to remember we were in a banking crisis in March. From an intermediate- to longer-term perspective, I don’t know why you wouldn’t want to protect yourself until this inflation cycle plays out.
Also read: Jackson Hole: Fed’s Powell could join rather than fight bond vigilantes as yields surge
More: Will August’s stock-market stumble turn into a rout? Here’s what to watch, says Fundstrat’s Tom Lee.
Source link
#Mother #Bubbles #crowd #doesnt #market #strategist #expects #stagflation #investing