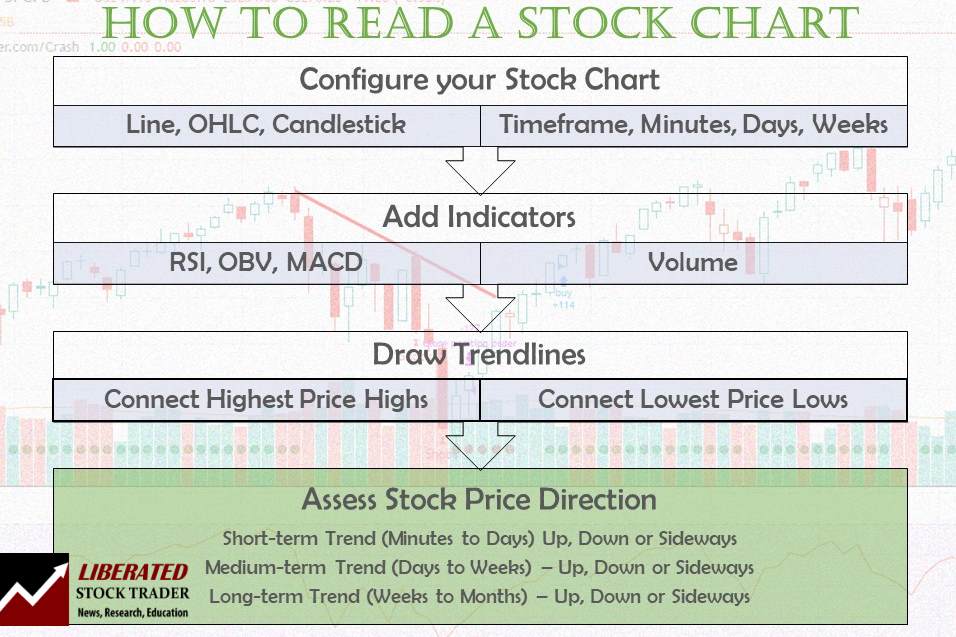
To read stock charts, you need to use stock charting software, select your chart type, configure your timeframe, determine price direction using trendlines, and use indicators to estimate future prices.
That may sound complicated, but as a technical analyst with the IFTA, I am certified in how to read stock charts, and I am here to help you learn. So I hope you enjoy this in-depth definitive guide to reading and understanding stock charts, patterns, and indicators.
What is a Stock Chart?
A stock chart visually represents the current and historical stock prices displayed on an X & Y-axis graph. Stock charts allow you to see the past and recent price performance of a company’s shares. Volume and price indicators are significant to stock charts and the ability to see historical price patterns and trends to predict future price movement.
To understand stock charts, you need to know how supply and demand work in a marketplace. The volume indicator and the stock price movement are the critical elements in effectively interpreting stock charts. For example, when the price rises on increased trading volume, you can expect the price to continue higher.
All of this will be covered in the volume, supply, and demand section.
How to Read a Stock Chart: 7-Step Process
Here is a quick and simple process for reading a stock chart:
- Open a stock chart: Use Free Charts
- Select a chart type: [Choose OHLC or Candlestick]
- Choose a chart timeframe & scale
- Assess price direction with trendlines
- Use Trendlines to Determine Price Patterns
- Add chart indicators: Moving Averages, RSI, OBV, MACD
- Estimate the Future Direction of the Stock Price
1. Open a Stock Chart
You can read stock charts using stock charting software that performs the data collection and calculations for you. You need to understand stock prices, timeframes, supply and demand, chart patterns, volumes, and how stock chart indicators are calculated. We cover the eight stock chart types, indicators & patterns in this guide.
To quickly open a stock chart for free and without registration, try TradingView.
This section is all about understanding a basic stock chart. Known as Technical Analysis or stock chart analysis, chart reading enables us to visualize a stock not through numbers but through patterns. It allows us to see the stock, and its history, learn its personality, and make a value judgment on its future. Before you get started learning to read charts, you might want to select charting software that is perfect for beginners.
We will start with a basic price chart, move on to technical indicators, and assess their importance and meaning in future sessions.
Invest in yourself! Get all our courses & strategies for 50% off
★ Liberated Stock Trader Pro Stock Investing & Trading Course ★
★ M.O.S.E.S. Market Outperforming ETF Strategy ★
★ LST Beat the Market Stock Picking Strategy ★
★ Exclusive Bonus Course – The Stock Market Crash Detector Strategy ★
★ Fully Guided Videos, eBooks & Lifetime Email Support ★
★ 108 Videos + 3 Full eBooks + 5 Scripts for TradingView & Stock Rover ★
All Star Pass Black Friday -50% Deal Is Live – Ends In:
2. Select a Chart Type
Stock charts come in many shapes and sizes, from the differences in the bars to the different concepts applied to the chart itself. Here you will find a quick reference guide to the many types of charts available with an overview of their potential uses. Click here for an in-depth guide to stock chart types.
1. Line Stock Chart
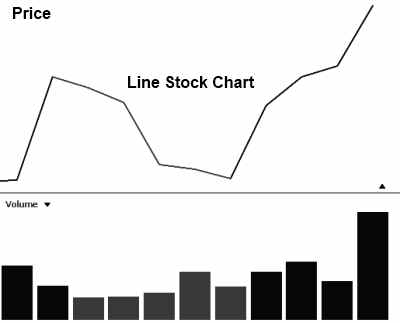
This is one of the most basic charts, probably giving the least amount of information. The line in the top pane is drawn using the close price for each unit of time. So if this is a daily line chart, the close price for the day is used. If this is a 5-minute chart, then the close price for every 5 minutes of trading is used.
The Positives of Line Stock Charts
A clear view of the price movement. Good to use when comparing the performance of many stocks on the same chart.
The Negatives of Line Stock Charts
It does not show the Price Open / High / Low for the trading period. The day’s trading range is important in price-based decision-making, indicating bullish or bearish momentum.
Stock Charting Software With Line Charts
- TradingView – Our Number 1 & Free Stock Charting & Analysis Package
- Stock Rover – The Best Software for Stock Screening for Investors
- TC2000 – Best For US Trading & Stock Analysis
- TrendSpider – Best For Automated Technical Analysis
2. High Low Close Bar Stock Chart (HLC)
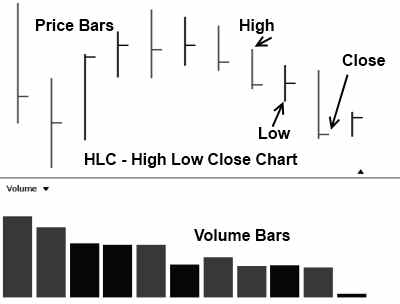
Using bars is a step up from the line chart as it allows us to plot additional useful data on the chart. Here we have each bar representing a trading period with the price High, Low, and Close represented. Refer to the diagram.
The Positives of High Low Close Bar Charts
More information is available, showing the days trading range, meaning did the stock price close near its high (bullish) or near its low (bearish)?
The Negatives of High Low Close Bar Charts
No opening price is reflected in this chart. The opening price is important as it allows us to immediately see if the price gapped up or down on the open and where the closing price is related to the opening price.
Stock Charting Software With HLC Charts
- TradingView – Our Number 1 & Free Stock Charting & Analysis Package
- Stock Rover – The Best Software for Stock Screening for Investors
- TC2000 – Best For US Trading & Stock Analysis
- TrendSpider – Best For Automated Technical Analysis
–
Video: Stock Chart Types Walkthrough
–
3. Open High Low Close Bar Stock Chart (OHLC)
The complete bar chart. The chart of choice for those who like to use bar charts. Here we see the day’s trading range, including the open and close prices.
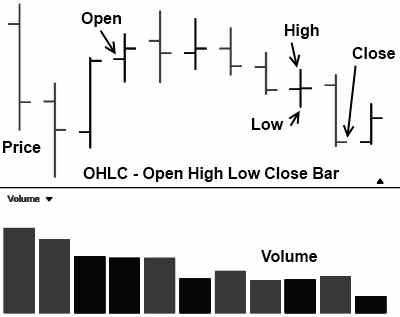
The Positives of Open High Low Close Bar Charts
We can see instantly if the trading period closed higher or lower than the open. We can also see the bar’s length, which shows us the trend’s volatility or strength.
The Negatives of Open High Low Close Bar Charts
There are a few downsides to this chart type, and many investors and traders use it. Most chart packages also allow you to color the up days green and the down days red. The following charts can also be used for those who prefer even more information in the price chart.
Stock Charting Services With OHLC Charts
- TradingView – Our Number 1 & Free Stock Charting & Analysis Package
- Stock Rover – The Best Software for Stock Screening for Investors
- TC2000 – Best For US Trading & Stock Analysis
- TrendSpider – Best For Automated Technical Analysis
4. Japanese Candlestick Charts (Recommended)
Used widely in Japan and gaining a strong foothold in the rest of the world, the Japanese Candlestick chart gives an excellent insight into current and future price movements.
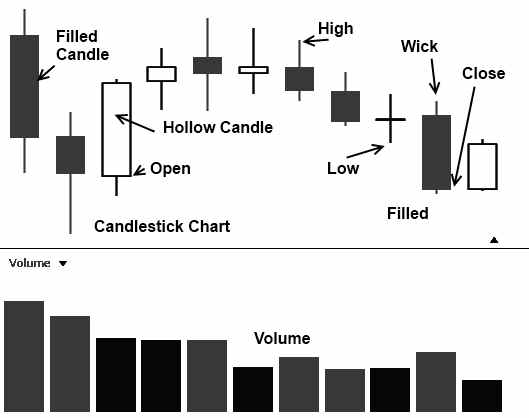
The Positives of Japanese Candlestick Charts
Candlestick charts give an excellent view of the asset price open, high, low, and close. Candlestick charts are visually illuminating and make market supply and demand easier to spot. Candlestick chart patterns allow us to judge the future short-term direction of price. Candlestick charts connect investor psychology with the price pattern.
The Negatives of Japanese Candlestick Charts
Although Candlesticks have many advantages, they can seem like information overload to the beginner. There are also many Candlestick patterns to learn.
Automated Candlestick Chart Recognition
Before you jump into a headlong three months of studying and analyzing Japanese Candlesticks manually, I highly recommend you use the power of modern stock charting algorithm software to recognize patterns for you.
Three of our recommended stock charting software have automated Candlestick pattern recognition that identifies and analyzes candlesticks better than humans.
Further Reading on Japanese Candlesticks.
Stock Charting Services With Candlesticks Charts
- TradingView – Our Number 1 & Free Stock Charting & Analysis Package
- Stock Rover – The Best Software for Stock Screening for Investors
- TC2000 – Best For US Trading & Stock Analysis
- TrendSpider – Best For Automated Technical Analysis
Stock Charts Using Volume
The use of volume in technical analysis is important as volume allows us an insight into the supply and demand situation. The following charts incorporate volume into the price window to provide additional information.
5. Volume at Price (VAP) Stock Chart
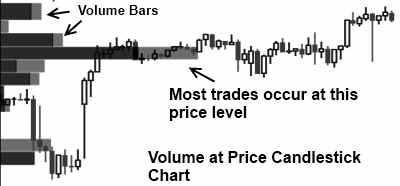
The price at volume chart is an exciting new development, as instead of showing volume for a certain time period, it shows us the volume of trades at a specific price level.
This lets us see at what price level most market participants believe the stock is fairly priced.
The Positives of the Volume at Price Chart
Innovative and intuitive, this charting method, combined with standard volume bars, can enable you to see market psychology both in time and price. It is also easy to see volume increasing as price rises; this is a very bullish sign.
The Negatives of the Volume at Price Chart
Not all stock charting packages offer this type of indicator.
Stock Charting Services With Volume at Price Charts
- TradingView – Number 1 Free Stock Charting & Analysis Package
- TC2000 – Best For US Trading & Stock Analysis
Beat The Market, Avoid Crashes & Lower Your Risks
Nobody wants to see their hard-earned money disappear in a stock market crash.
Over the past century, the US stock market has had 6 major crashes that have caused investors to lose trillions of dollars.
The MOSES Index ETF Investing Strategy will help you avoid or minimize the impact of major stock market crashes. MOSES will alert you before the next crash happens, so you can protect your portfolio. You will also know when the bear market is over, so you can start investing again.
MOSES Helps You Secure & Grow Your Biggest Investments
★ 3 Index ETF Strategies ★
★ Outperforms the NASDAQ 100, S&P500 & Russell 3000 ★
★ Beats the DAX, CAC40 & EURO STOXX Indices ★
★ Buy & Sell Signals Generated ★
MOSES Helps You Sleep Better At Night Knowing You A Prepared For Future Disasters
6. Point and Figure (P&F) Charts
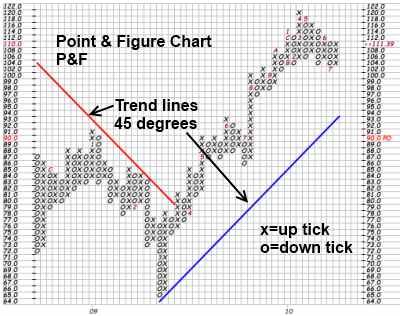
There are a few other types of charts that you probably have never heard of before. However, they are quite useful, and you would be required to learn them if you wanted to become a Certified Technical Analyst.
Point & Figure Charts are very unusual as they feature no timeline along the bottom horizontal axis. The chart is made up only of price swings. The vertical price bar is arithmetic and shows only units of price.
A “0” is plotted if the price moves down a whole price unit (for example, 50 cents). When the price changes direction and starts to move upwards, an “X” is marked in each box. This filters out smaller price moves and enables us to focus on trend quality.
Trendlines are always plotted either horizontally or at 45-degree angles.
The Positives of Point & Figure Stock Charts
An excellent tool for doing price target calculations. Simple to learn and interpret, few price patterns to learn.
The Negatives of Point & Figure Stock Charts
Learning this type of charting can be easiest when performing the charting by hand. That means you are marking the “X” and “O” on a piece of paper. This can also be very time-consuming. Few services offer Point and Figure Charts. However, StockCharts.com offers a free Point and Figure Charting Service that is well worth investigating.
Stock Charting Services With Line Charts
- TradingView – Number 1 Stock Charting & Analysis Package
7. Market Profile Stock Charts
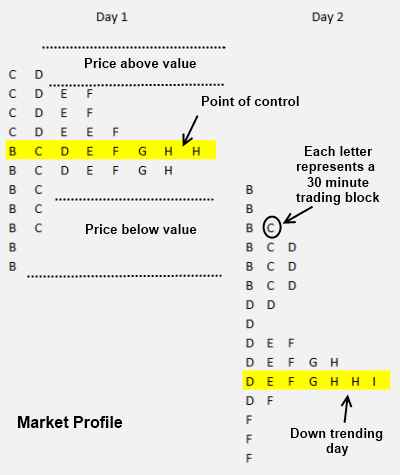
Developed in the 1980s by Chicago Board Of Trade Pitt Trader J. Peter Stiedlmayer. The letters on the chart show time units. “A” represents the first 30 minutes of trading, and “B” represents the second 30 minutes of trading.
The point of control is the area (price range) where most trades occur during the day.
The value areas are the price range at which 70% of the action happens. When the price is above and below the value areas, this represents a possible ideal buying or selling point.
The Positives of Market Profile Stock Charts
People who use market profile charts become evangelists for the cause. They believe it offers unique insights into buy and sell opportunities. It can be a good option if you are a quick-fire day trader.
The Negatives of Market Profile Stock Charts
It can require an effort to learn how to use them, and very few stock chart services offer this type of charting.
3. Choose a Chart Timeframe
Core Elements of a Stock Chart
- Ticker & Company Name: What company stock price are you looking at
- Chart Type: What chart are you using, Bar, Line, or Candlestick?
- Time Frames: Daily, Weekly, Monthly, or Yearly
- Chart Scaling: What scale is price using, Percent, Fixed, Algorithmic, or Logarithmic
- Price Bars: Indicate the Open, High, Low, and Close of the price for the day
This is a historical price chart of Intel Corp. (Ticker: INTC). Once you understand what each of these arrows means, you are ready to step forward into the technical indicators section.
Understanding a Stock Price Chart – Open, High, Low, Close, TimeFrame, Ticker & Scaling
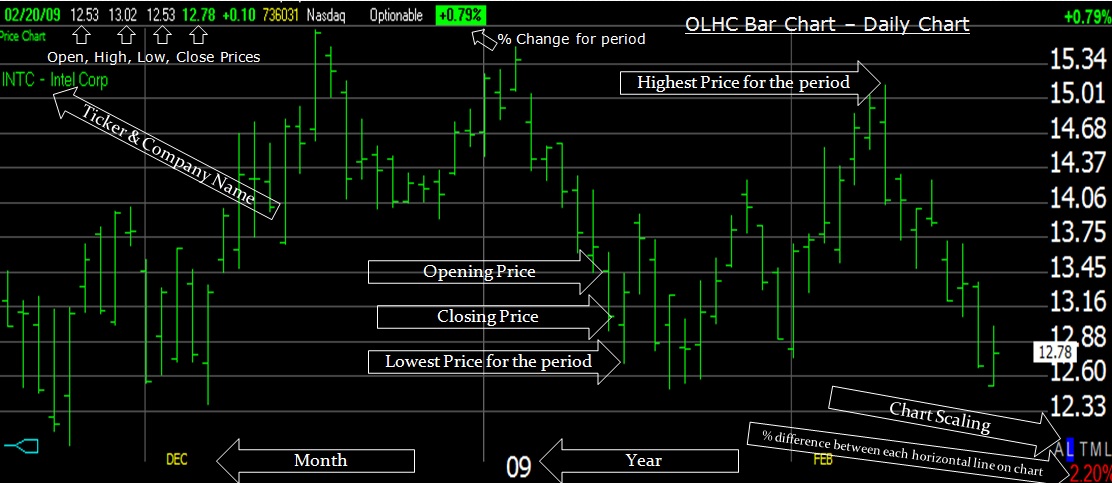
This chart is in the format of a Daily “Open High Low Close” OLHC bar chart, mapped to the Logarithmic Scale.
Ticker & Company Name
The ticker (INTC) is the unique abbreviated stock reference code; all stocks have a unique Ticker to be easily found and referenced.
Chart Type
There are many different types of charts available; this one is an OLHC Chart, which means “Open, High, Low, Close.” OHLC refers to the bar itself. The opening price is the left-sided dash, High is the top of the vertical line, Low is the bottom of the line, and Close is the right-sided horizontal dash. Read more about stock prices.
Time Frames
Timeframes are always plotted along the chart’s bottom and can be anything from 1-minute per bar (intraday) to 1 year per bar. This chart shows a Daily chart, which means each bar equals 1 day.
Chart Scaling
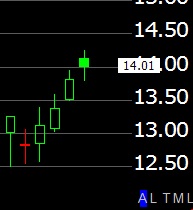
Chart Scaling is critical; most professional chart readers use the “Logarithmic Scale,” meaning each unit along the right-sided Y-Axis is the same percentage apart; this makes it very easy for you to see on the price chart what percentage a stock moves on any given day in history.
If the bottom right-hand side of the chart shows a 2.20%, this is the % between the horizontal Plotlines.
Arithmetic Scale.
The other key scale is the “Arithmetic Scale,” which shows a fixed price in the Vertical Y-Axis; in this example, the scale increments every 50 cents, $12.50, $13.00, etc.
4. Assess Price Direction Using Trendlines
To read a stock chart, you need to draw a trendline on the price pattern; this helps you assess the direction of the stock price.
What is a Stock Price Trend?
If someone asked you today, “Is the stock market in an uptrend, downtrend, or a lateral consolidation,” what would you answer? Knowing the answer to this key question is important for the stock market or even an individual stock. Why?
If you buy a stock (go long) in an uptrend, you are more likely to make money on it. There is a simple way to see if the market is heading upwards or downwards.
First, let’s examine what types of trends exist:
3 Types of stock price trends:
- Uptrend: The stock or index is moving up, making new highs or higher highs
- Downtrend: The stock or index is moving downwards, making lower lows
- Sideways consolidation: neither making significant new highs nor new lows
There are also timeframes to consider in evaluating a trend; for this, we will refer to Charles Dow’s classification in Dow Theory.
Types of Stock Trend Timeframes:
- Short Term: Days to weeks
- Medium Term: Weeks to months
- Long Term: Months to years
By combining the above terms, you could be specific about the market trend. For example, you could say the market is in a short-term up-trend but a long-term down-trend. But isn’t that contradictory, the market being in both an uptrend and a downtrend simultaneously?
Not really it makes perfect sense.
Investing In Stocks Can Be Complicated, Stock Rover Makes It Easy.
Stock Rover is our #1 rated stock investing tool for:
★ Growth Investing – With industry Leading Research Reports ★
★ Value Investing – Find Value Stocks Using Warren Buffett’s Strategies ★
★ Income Investing – Harvest Safe Regular Dividends from Stocks ★
“I have been researching and investing in stocks for 20 years! I now manage all my stock investments using Stock Rover.” Barry D. Moore – Founder: LiberatedStockTrader.com
Get Stock Rover Premium Plus Now or Read the In-Depth Stock Rover Review & Test.
The Following Examples are an excerpt from the Liberated Stock Trader Academy Book and Training Course. Chapter 7, Section 2.
How to Draw Trendlines on the Stock Price
Drawing trendlines is one of the most important skills of technical analysts; trendlines represent important areas of support and resistance. Once you have this skill, charts come to life and start to signal their message to you.
Video: How To Draw Trendlines
Please excuse the sound quality – it was a live broadcast.
3 Steps to Drawing your First Trendlines
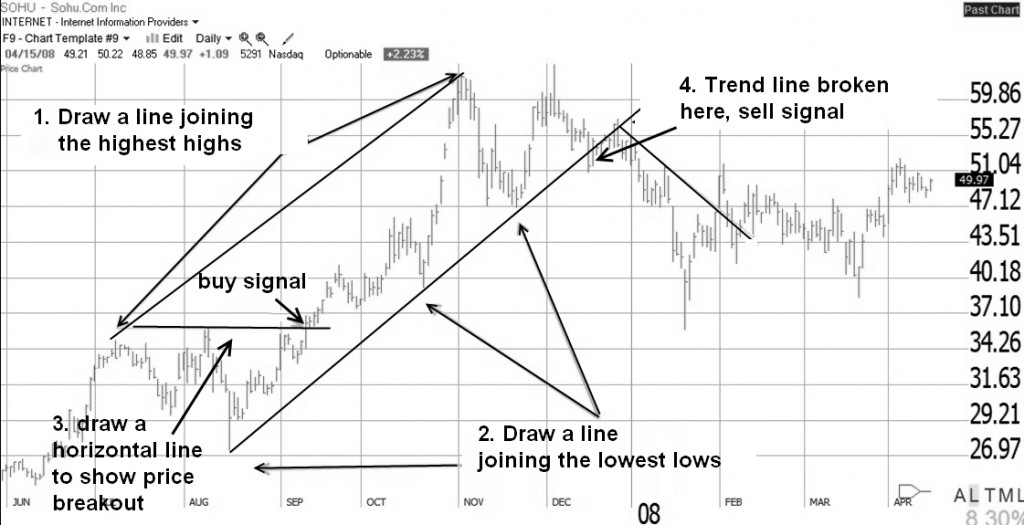
1. Drawing Uptrends
- To evaluate an upward trend, draw a line joining the highest highs
- For the floor of the uptrend, draw a line connecting the lowest lows. The price here bounces 3 times off the bottom line but proceeds higher.
- A trendline is drawn to show that the price has moved strongly past the previous high; this is a BUY Signal at $35.50.
- Finally, the price is exhausted and falls through the bottom resistance line at $51. This break of the upward support line is a sell signal.
Quick Tip: The more bounces off a trendline the stronger the trend.
Based on the trendlines shown here, buying and selling would have bagged you a 49% win. Life is never that easy, and showing this in retrospect does mean we benefit from hindsight.
2. Drawing Support & Resistance Trendlines
You must practice drawing trendlines as much as possible; after a while, you will get used to it, and it will become second nature.
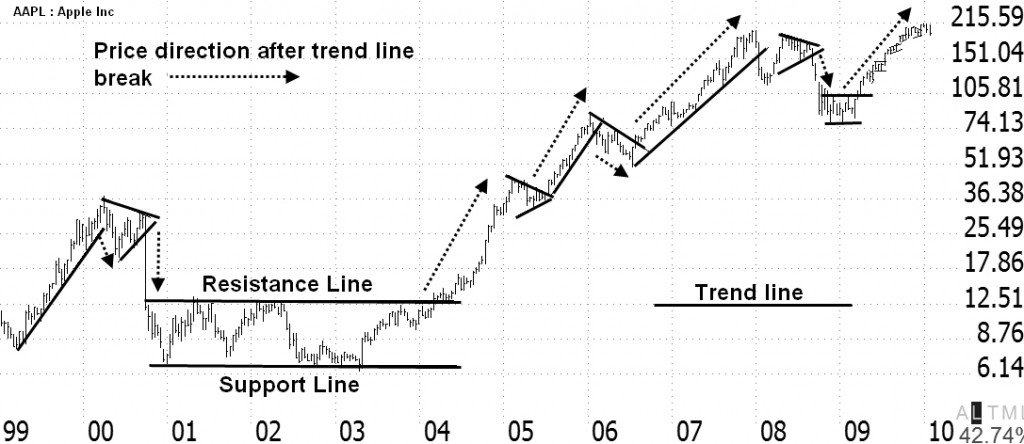
Here is another example of how to draw trendlines. This is a chart of Ticker: AAPL Apple Inc. it shows how to draw trendlines in a downward price move and an upward price move.
Notice that the trendline above the price is called resistance, and the trendline below the price is called support. When the price breaks up through resistance, it moves higher; this could potentially be a buy signal. When the price breaks down through the support trendline, it moves lower; this could potentially be a sell signal.
Quick Tip: The longer the trendline is in place or acts as support or resistance, the stronger the trend and the bigger the move when the trendline is broken.
Look again at the chart of Apple Inc. See how Apple was in a sideways consolidation from 2001 through to 2004. When it eventually broke out of that channel upwards through resistance, the stock took off, making over 1600% gain.
Chapter 7 of the PRO Training delves deeper into the technical analysis to enable you to make Buy and Sell decisions using trendlines, spot the most important patterns and trends, and discusses the importance of Price Gaps, Triangles, and Wedges.
5. Use Trendlines to Determine Price Patterns
Drawing Trendlines to Recognise Stock Chart Patterns
If you cannot draw a Trend-line you should not invest in the stock market!
This example will examine how to look at price movement and use it to evaluate the stock.
Price is the most important indicator, so it should be when it boils down to it; the most important thing is the price.
Here we can see a Broadcom (BRCM) chart, one of the darlings of the tech bubble in 2000.
Where will you draw the trendlines?
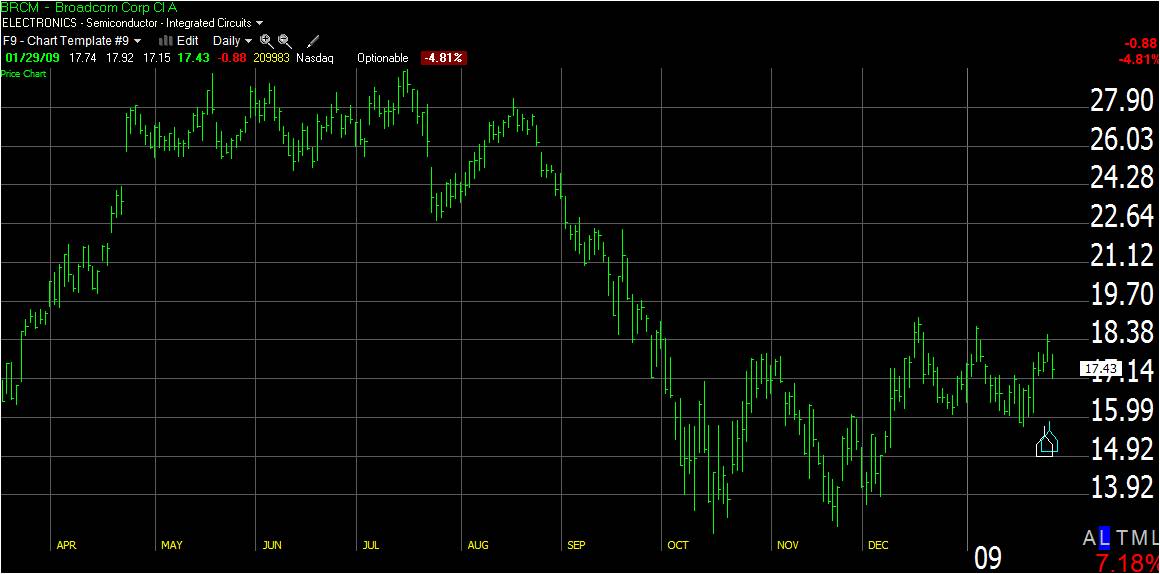
Take a moment to think about where you would draw the trendlines before scrolling down to the chart where I have drawn them.
Support & Resistance and a Double Bottom Pattern Trendlines
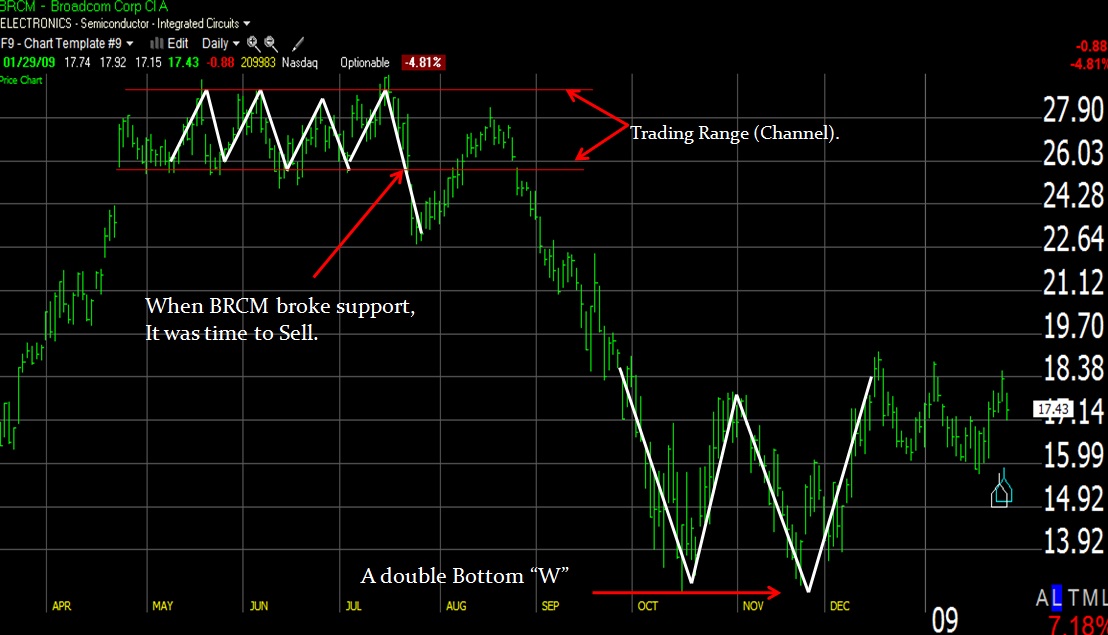
A chart can come alive when we add trendlines. The graphic below shows BRCM with trendlines superimposed.
Follow This Process to Draw the Trendlines
- From left to right, we see from mid-April to July that the stock starts to move in a sideways pattern known as “Channeling.”
- The two red lines show the “trading range”; this is the range between which the stock price fluctuates.
- The upper line is the Ceiling or the “Line Of Resistance,” and the lower line is the Floor or “Support.” Both lines show where the number of sellers equals that of buyers.
- The trend changes when the stock price falls through the support line, and a new market impetus affects the stock. If you owned this stock in April and enjoyed the corresponding price rise, this break would be a strong “Sell Signal” to the trained eye.
- The stock consequently dropped in 2 days and had the good courtesy to rise again over the following month to give anyone slow on the uptake another chance to Sell. It broke through the previous support line but was not strong enough to make it to the channel’s upper ceiling. If you had not gotten out this time, you would have suffered a punishing 50% loss. Enough to make a grown man weep!
- The next significant point to note is in mid-October when the stock bounces at about $13, clearly oversold, and proceeds to make a very nice looking “Double Bottom” or “W” bottom.
- Chartists worldwide recognize the double bottom, and those who like to buy on Bottoms would have done. This clearly happened as the stock moved up 38% in 3 weeks.
Learn To Recognize These Price Patterns
The first example in this module will show you the head and shoulders pattern. We will then discuss the other patterns that exist.
Head and Shoulders Pattern
What does a Head and Shoulder Pattern look like? The importance of the head and shoulders pattern should not be underestimated; it is one of the most reliable patterns in technical analysis yet one of the most misunderstood.
Here we discuss the famous head and shoulders price pattern. Understood to be one of the most predictive patterns, the Head and Shoulders pattern has unique characteristics.
However, you do need to know what you are looking for.
A Head & Shoulders Pattern has the following traits.
- Two shoulders.
- A high point, the head, in between the shoulders.
- The volume should confirm the pattern.
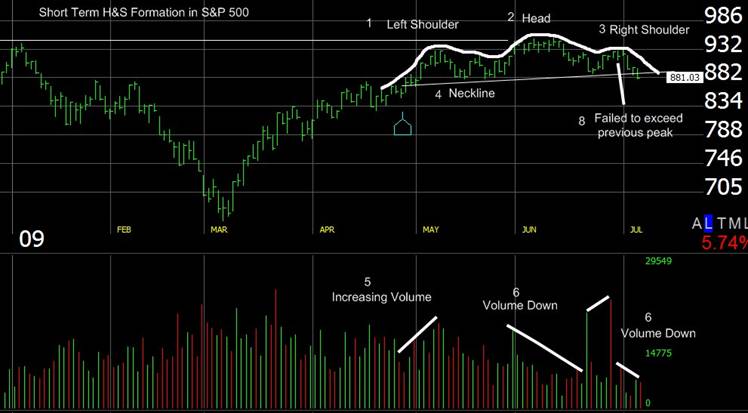
So what lessons can we learn from the chart?
- This is the left shoulder.
- This is the head
- This is the right shoulder.
- This is the neckline; using a trendline, connect the low from both sides of the head through the outer price limes.
- The left shoulder was formed on increasing volume. This is to be expected.
- In the forming of the head, we see a significant decrease in volume.
- In the right shoulder, we also see a decreasing volume.
- The price failed to exceed the previous peak.
All of the above conditions of the Head & Shoulders pattern are consistent with textbook descriptions.
The Head and Shoulders pattern is said to be confirmed on a break of the neckline; this is about to occur/has occurred in the final price bar in July.
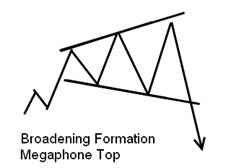
Megaphone Chart Pattern![Megaphone Top - Broadening Formation How to Read Stock Charts Like a Boss: Beginners Guide +pdf - 16]()
Here we have a Megaphone Top. This is a rare pattern that usually occurs at major tops. You can see that the swings get larger at each bounce, suggesting uncertainty and volatility until, finally, the price breaks out downward on increased volume.
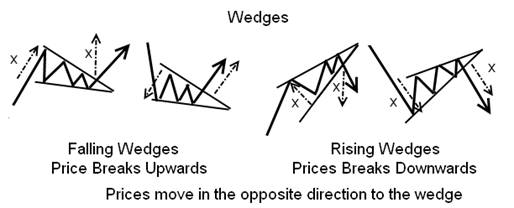
Wedge Chart Pattern
Wedges are very different from triangles because they point in the exact opposite direction to the breakout. Both of the edges of the wedge point in the same direction, either upward or downwards. In the image below, we can see that the falling wedges signify an upward breakout.
The rising wedge signals a downward breakout.
Stock Chart Pattern Accuracy
The following diagram shows us the most common reversal patterns and their relative probability of accuracy.
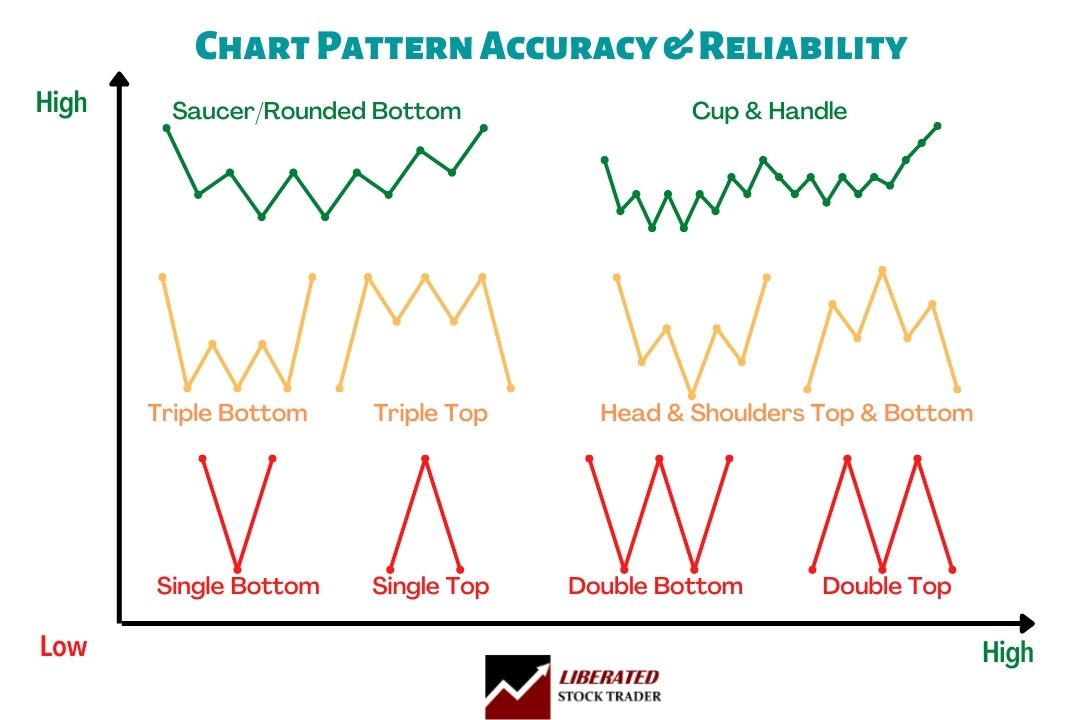
Price patterns and trendlines share the same characteristics. The longer they are, the more important they are. The more a price pattern touches a trendline and reverses, the more important that line is. This diagram shows that a Triple Top’s accuracy is more than that of a Single Top. Why? Because the price touches the resistance level more times.
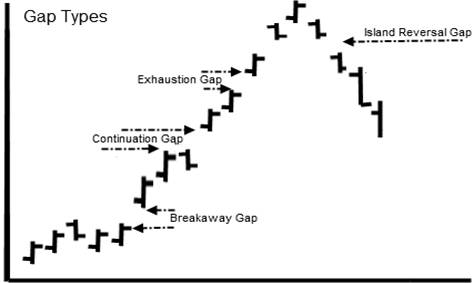
Gaps in Stock Chart Patterns
Another significant pattern that signals continuation is the “gap.” A gap occurs when a stock’s price during a given period is significantly higher or lower than the price range of that stock for the previous period. The price did not overlap at all over the two periods. This leaves what is known as a “gap” in the price chart. “gap up” in the stock price is a show of strength. This tells us that the demand for the stock was so strong on the open that it jumped many points higher. The opposite is true for a “gap down.” This signifies weakness as the stock gaps down usually due to aggressive selling.
The Breakaway Gap
The Breakaway Gap usually occurs when a stock moves normally through a price range or channel, then the demand for the stock explodes, and the stock “gaps out” of the current trend. This is a sign of strength and a very bullish sign with a “gap up.” A breakaway gap to the downside is a sure sign of weakness.
The Continuation Gap
The Continuation Gap is another sign of strength, showing that demand is still strong and the trend will continue; this often confirms the initial “breakaway gap.”
The Exhaustion Gap
The Exhaustion Gap can be the second or third gap and occurs during a powerful upsurge in price. This is a warning, as it might signify that the stock has overextended itself and may be due to a change in trend or a pullback. The opposite is true for an exhaustion gap on the downside, which might signal a bottom is near.
The Island Gap
The Island Gap occurs when demand is so high that price and the market participants drive the price up to unacceptable levels, and the demand dries up rapidly. This sudden oversupply causes the stock to plummet as all demand is satiated. Of course, too much supply with no demand causes falling prices.
Quick Tip: Gaps are important signs of serious shifts in supply and demand. If surges in demand outstrip the supply, prices rise to convince people on the sidelines to sell. Downside gaps indicate supply is outstripping demand, causing prices to fall.
This might seem very theoretical, so here are gap patterns in action.
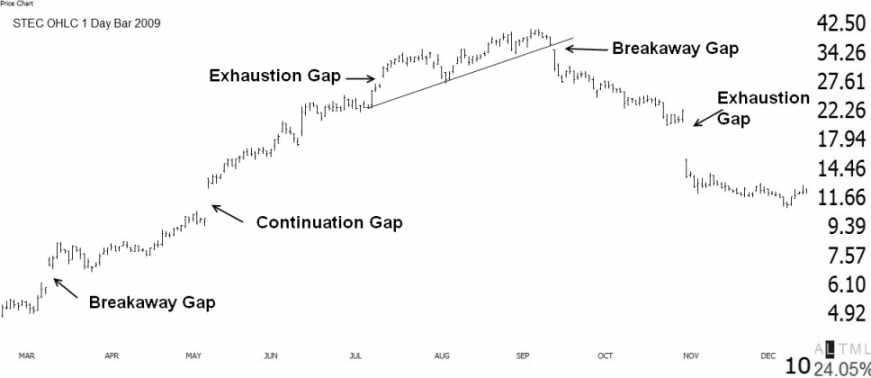
Examples of Stock Chart Gaps
Here we can see clearly how gaps can occur in stocks. TEC provides a perfect example of how understanding gaps is critical to trading success.
Stock Chart Continuation Patterns
Continuation patterns occur during a price move and are visual representations of consolidation or rest periods before the price continues its trend, be that upwards or downwards.
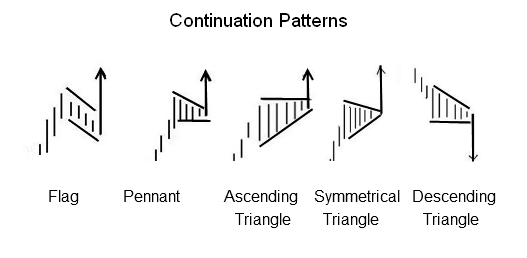
Image courtesy of Liberated Stock Trader PRO Training. ll rights reserved
All of these triangles are essentially continuation patterns. They should give you some confidence that the trend will continue. Always be aware that if the price breaks out in the wrong direction due to a shock (e.g., bad earnings or bad news), you should be prepared to act.
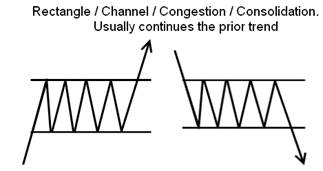
A widespread continuation pattern is the Rectangle, more commonly known as a “channel” or “trading range.” The price should normally break out in the same direction as the previous trend.
6. Add chart indicators
Indicators are lines that get plotted on a stock chart to make it simpler to understand the history and perhaps the future direction of a stock. Stock chart indicators consist of 2 key data points, price, and volume. However, it is also possible to map fundamental financial data such as EPS or PE ratio onto a chart.
Indicators may seem like something only Einstein himself can master. Here everything is within reach; you will have a solid understanding of a fundamental concept in just a few minutes.
Chart Indicators: Moving Averages
What are Moving Averages?
Moving averages are the staple diet of any chart reader and enable you to visualize changes in price trends. Moving Averages (MA) are simple mathematical calculation that takes the average price (mean) for a given period and plots this on a chart.
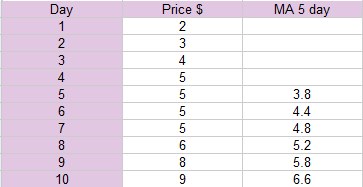
So the average price for the first five days = 3.8.
The key here is when we use 2 or 3 moving averages together, we see visually when the lines cross a stock’s trend is changing, and it may be time to look seriously at buying or selling a given stock.
Using 3 Moving Averages Together
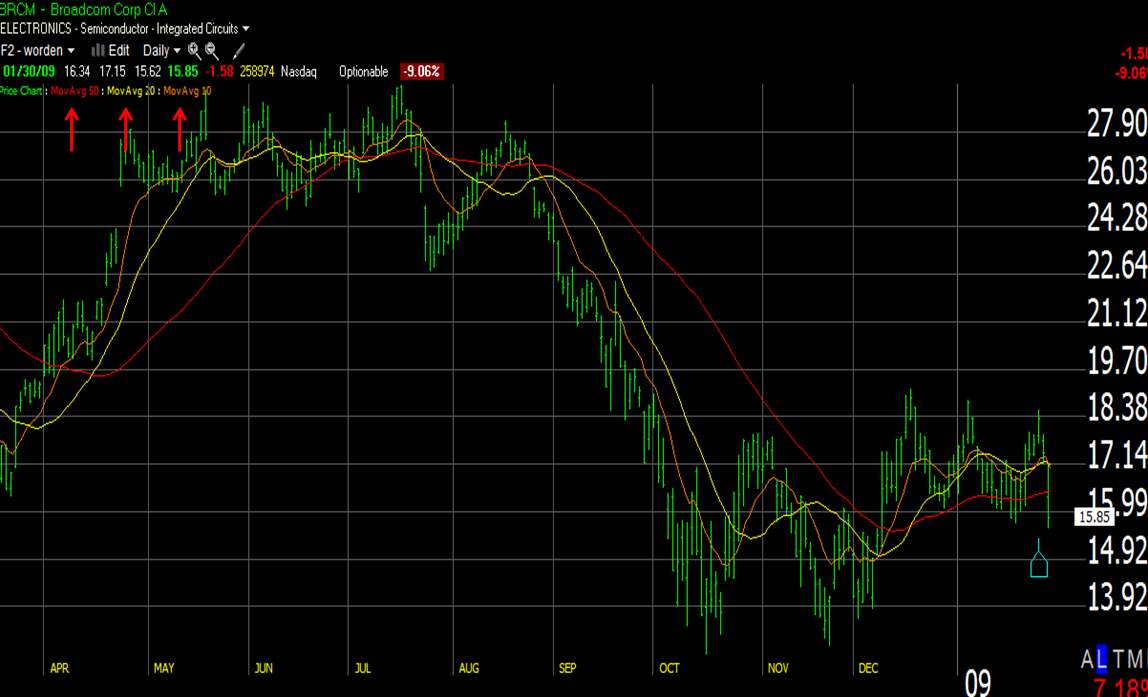
Below you can see a standard chart with three moving averages plotted.
MA50 (RED) – this is the moving average of the last 50 periods (in this case, days – it is a daily chart)
MA20 (Yellow) – this is the Moving Average of the last 20 days
MA10 (Orange) – this is the Moving Average of the last 10 days
The secret is the combination of the indicators.
What do you see here? Take a long look!
- Where do the lines cross?
- What happens to the stock price after the lines cross?
- What happens to the overall trend when the lines cross?
How to use Moving Averages to signal BUY and SELL opportunities?
We are using 3 Moving averages; you could use 2; however, 2 is the minimum. You can set different moving average timeframes; common ones are: 10:20:50:200 day MA’s
If you are trading more short-term, use the lower Moving Averages. If you buy and hold a stock for 6 months or more, use longer averages.
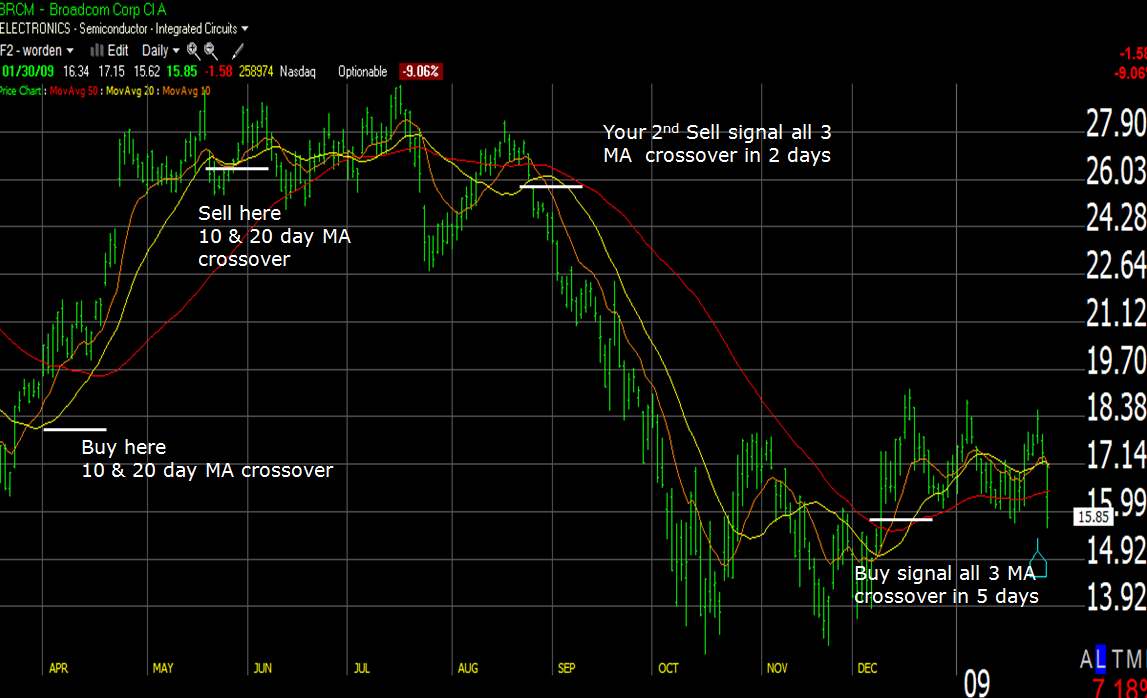
As you can see, when the MA’s cross, this is the pivotal point that signals a change in trend.
Of course, you can backtest the moving averages to see if they work on a previous timeline (by scrolling backward in the chart). Use them as a minimum indicator to help you envisage when a stock will move in your favor or move against you.
Moving averages are an excellent indicator as they are based on price, and price, as we know, is the most important of all indicators.
What Did You Learn About Moving Averages?
Moving Averages are the core and fundamental element of Technical Stock Chart Analysis. Using one MA is good; using three is a lot better.
Focus on the moving average lines crossing each other and the price crossing up or down through the moving average lines.
Chart Indicators: Volume
Volume in stocks refers to the total number of shares traded for a particular period of time. If 2 million shares are traded in a day, the day’s trading volume is 2 million.
What Does Volume Mean in Stocks?
Volume is usually expressed as a series of vertical bars at the bottom of a chart. If 20 shares were traded, then the bar will show 20,000. Volume charts will often show Red Bars when the stock price has decreased for the day and Green Bars when the price rises for the day.
Is the Volume Indicator Important?
Yes, Volume indicators in technical analysis are considered important, second only to stock price itself. Then you combine the stock price movement with the increases or decreases in volume; it provides a fascinating insight into the market’s sentiment.
For example, if the stock price is going up and the volume is going down, that indicates fewer people are buying at a higher price. This means a change in demand and a potential change in the direction of the stock price.
Understanding Trading Volume
Look at the chart below and read further for a description of the key concepts. The chart maps price, moving averages 10 & 30, and volume (red for negative, green for positive).
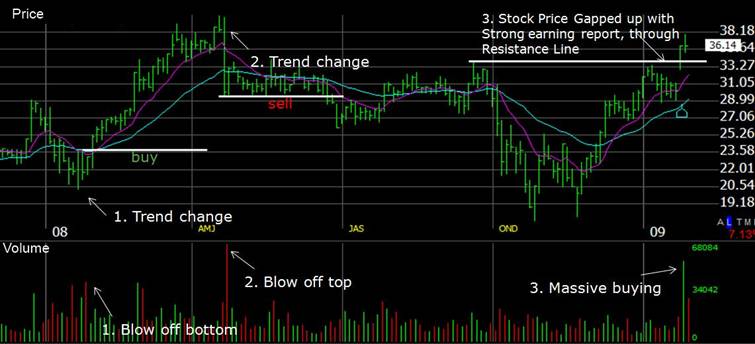
3 Key Steps Referenced in the Volume Chart.
1 – Price Direction Changes Upwards – Surge In Volume
Here at point 1, we see a huge change in the direction of price; it was proceeding downward, then suddenly, there was a spike in volume over two weeks; this is known as a “blow-off bottom.”
It indicates that a key price has been found, where the sellers have lost enough that they need to sell the stock, and the buyers have seen the price decrease enough so that they see real value in the Stock. Of course, other factors contribute, like good news or earnings results. Whatever happened, the volume increased!
2 – Price Direction Change Down – Surge In Volume
The stock increases from $20 to $38 in the following three months, a 90% increase, but how would we know this was about to happen? Well, buying when the moving averages crossed over would have been a good option; it would not have provided the full 90%, but it would have produced 40%, which by anyone’s reckoning, is an excellent result. However, here we see a monster, “Blow off Top,” the huge red Spike; this is a powerful sign to sell as soon as possible.
From stage 2, we see the stock move in a sideways pattern and eventually decrease back down to $19; the ride is well and truly over. However, you would not own the stock, as you would have sold when the moving averages crossed.
The stock price starts to increase in mid-November 2008, but volume tells us nothing.
WHY? Indicators do not tell us something 100% of the time, but we need to recognize it when they do. The moving averages cross at $25, a good time to buy.
3 – Huge Volume and Price Increasing
Here we see massive buying; the volume goes through the roof. Important to note is that we are comparing volume of the stock in comparison to its history. This is the second biggest volume surge of the year for Netflix and is significant.
Why did it take off? We should always seek enlightenment!
It reported excellent earnings, and because of the recession, people were switching from buying bigger ticket items such as Cars and Plasma TVs to staying at home and renting movies. Netflix reported a massive increase in new members.
In the chart, this note shows that the price “Gapped Up.” What does this mean? This means that the stock price in extended-hours trading was so strong that the Opening Price on the following day was significantly higher than even the High for the previous day, thus showing a gap in the chart’s price pattern.
Warning: Some volatile stocks show a lot of Gaps in price. While price gaps might sound good when they gap upwards, if they gap down against you, then they are very bad. Avoid stocks with any history of strong negative gapping, as gaps do not allow you to sell at the price you want to.
Volume Summary
Volume is important, and reading it should become second nature. When searching for winning stocks, we ideally should look for stocks with increased volume so we have more chance of a quicker, less risky win.
Is it Good to Have a High Volume in Stocks?
It depends. High volume when the price decreases means there is a large sell-off happening. When the stock price is going up, high volume means there is a rally in the stock price, and there is a great demand for the stock.
What is a Good Volume in Stock?
Try to stick to trading stocks with at least $1 million traded per day. That means (Stock Price * Volume) = $ Volume Traded. There is another easy way to see if a stock has enough volume. If you see large gaps between the open and closing price for any stock, there is not enough liquidity in the stock. This means not enough volume.
Penny Stocks often do not have enough volume. For example, if the stock price is $1 and the volume is 5,000, that means only $5000 of stocks is traded in a single day; that is not a fair and equitable market.
Volume – Supply & Demand
There are some important characteristics of volume and price in the marketplace. It is all about price movement direction compared to the increases or decreases in volume. In short, it is about Buyers and Sellers.
Price Up–Volume Up Stock Price moves higher on increased volume. This is bullish as it shows us that more participants are interested in selling the stock at higher prices and that, most importantly, more people are interested in buying the stock at those higher prices. In an uptrend, this signals the trend will continue; in a downtrend, this signals a possible correction or change in the trend’s short-term direction to upwards.
Price Up-Volume Down in an uptrend is very bearish as it suggests that although prices are rising, fewer participants suggest people are backing away from the higher prices. This also infers that the trend is weakening. In a downtrend, it suggests a continuance of the downtrend.
Price Down–Volume Up in a downtrend may signal that a change in trend is likely; as we saw with the “Blow off bottom,” there might be a huge selling climax, then the trend adjusts from down to sideways or down to up. This may indicate a crisis, panic selling, or simply when a stock is going out of favor in an uptrend. The pressure is on the sell side, and to sell, they have to accept lower prices. A strong negative signal!
Price Down–Volume Down in a downtrend can suggest that the retreat is slowing or beginning to end as fewer people are interested in buying or selling the stock at these prices. In an uptrend, this may indicate the stock is stopping for a breath or due to a pullback before continuing on its upward trajectory. Volume tends to trend in the same direction as the price trend, so PDVD also suggests a continuation of the main downtrend or a pullback and a possible continuation of an uptrend.
So you see, not only the price but the direction of both price and volume is important. This is where the Price Volume Indicators play an important role.
RSI Stock Chart Indicator
Here we have a popular indicator called Relative Strength Index, or Wilders RSI. Developed by J Welles Wilder, this indicator measures any stock’s strength by comparing its average net up closing day prices versus its average net down closing prices for the period set. It enables you to see if a stock is overbought or oversold.
How Is the Relative Strength Indicator Calculated?
RSI fluctuates between 0 and 100, 0= Oversold and 100 being overbought. It is a leading indicator and can be used to predict future trend changes using positive or negative divergences compared to price.
Divergences are one of the most powerful ways to use most indicators. It is a leading indicator, as opposed to Moving Averages, which are lagging, and can thus indicate future directional changes.
Relative Strength 5-Step Detailed Analysis
The chart below is of Smith & Wesson (SWHC), a stock I bought back in 2009, and the chart clearly shows how RSI can be used to predict future trend changes.
Using RSI on two settings shows how shorter and longer-term settings can show a different line but the same answer, confirming each other.
- The shorter-term setting (7 Periods Prices:7 Periods Smoothing)
- The longer-term setting (14 Periods Prices:7 Periods Smoothing ).
Review the chart, and read below the five key points explaining usage.
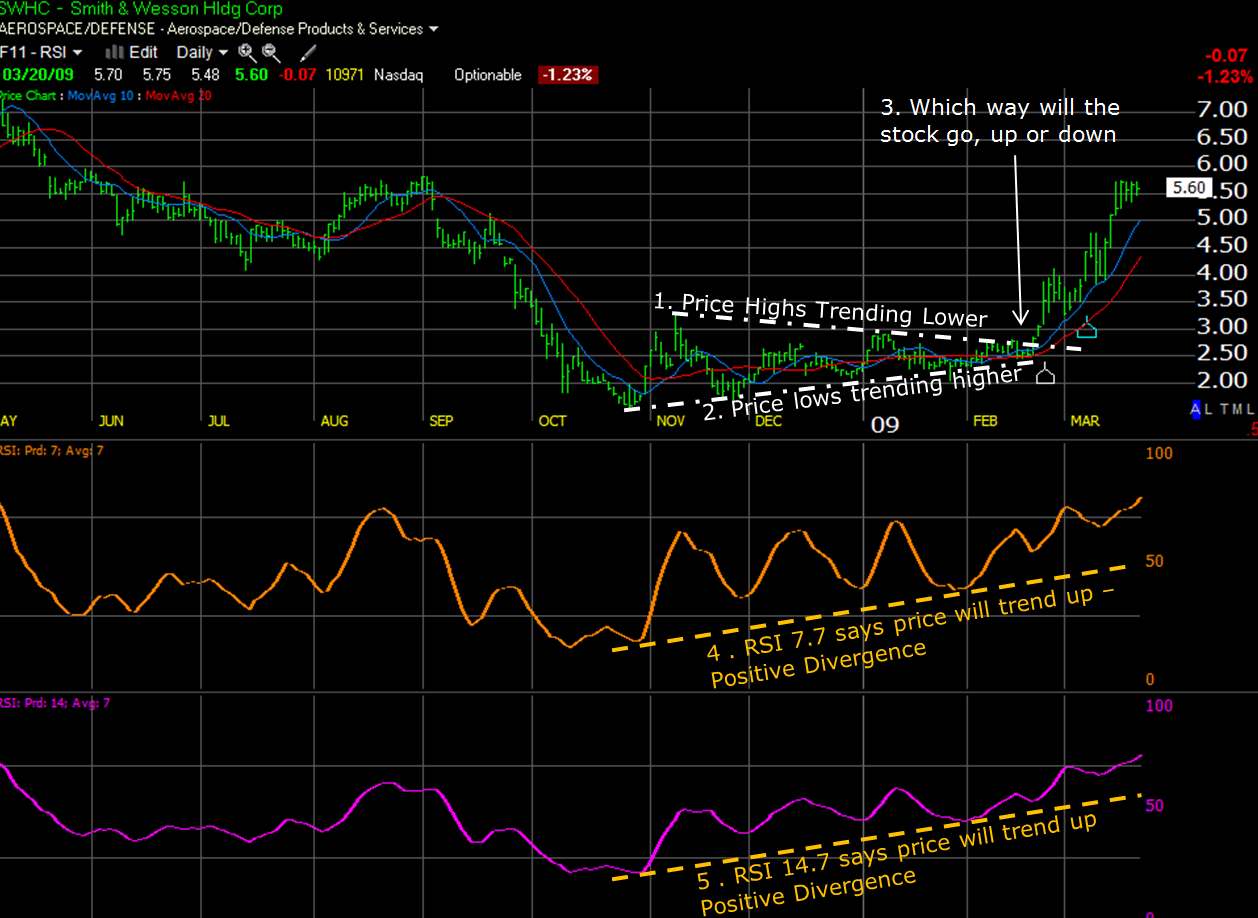
TC2000 chart courtesy of Worden Brothers, Inc.
- Here you can see the price highs trending downward from the period November 2008 to February 2009
- Here we see the price lows trending higher for the same period.
- So we see the forming of a Price Pennant, but which way will the Stock price go? Up or Down. For the answer, we refer to the leading indicator, RSI.
- The RSI (7:7) Orange line tells us as early as the beginning of January 2009 that we see stronger upward momentum in RSI; although this is not reflected in the Price, it is the underlying action.
- The RSI (14:7) also confirms the shorter timeframe RSI settings but gives us a smoother line that can be easier to interpret.
Finally, in mid-February, the stock price bursts through the price high trendline (point 1 above), and the stock proceeds to double in Price (100%) in 5 weeks.
What a great result and proof that RSI has real meaning and application.
However, if RSI tells you nothing important, please use other indicators or review another stock where the indicators will tell you something.
To control your investment, your money, and your destiny takes hard work, but the fruit will be sweet.
MACD Stock Chart Indicator
MACD, or Moving Average Convergence Divergence, is a great way to assess a stock price direction.
What is MACD?
Gerald Appel developed MACD to easily show the Moving Averages of stock in a way that could show the strength of the difference in the Moving Averages. For example, if the 10 & 20-day moving averages for a stock move away from each other as the stock goes up, this means the stock is gaining strength.
MACD Usage
Short = the shorter Moving Average, e.g., 10
Long = the longer moving average, e.g., 20 or 30
Period = the Moving average of the difference between the Short and Long above.
Use short MACD configuration for shorter-term trading 5-35-5, or longer configurations for longer-term trading 12-26-9 is popular, also 10-30-5.
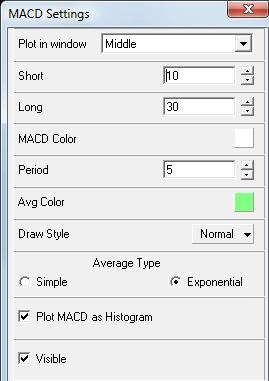
Experiment and view charts on different timeframes to test if the indicator is true from different angles.
This could go on and on; however, I will suggest now we move to the more practical use of MACD, viewing it in real life on a real stock.
Please be aware that sometimes MACD does not tell you anything about a stock, but it does in many cases. If the indicators tell you nothing, there is probably nothing to be told; move on and look for other stocks.
How to Use MACD
Take a look at the Netflix (NFLX) Learning Chart below.
Here we have a MACD configuration of 10, 30, and 5 Simple, and this is a 2-Day (per bar) chart.
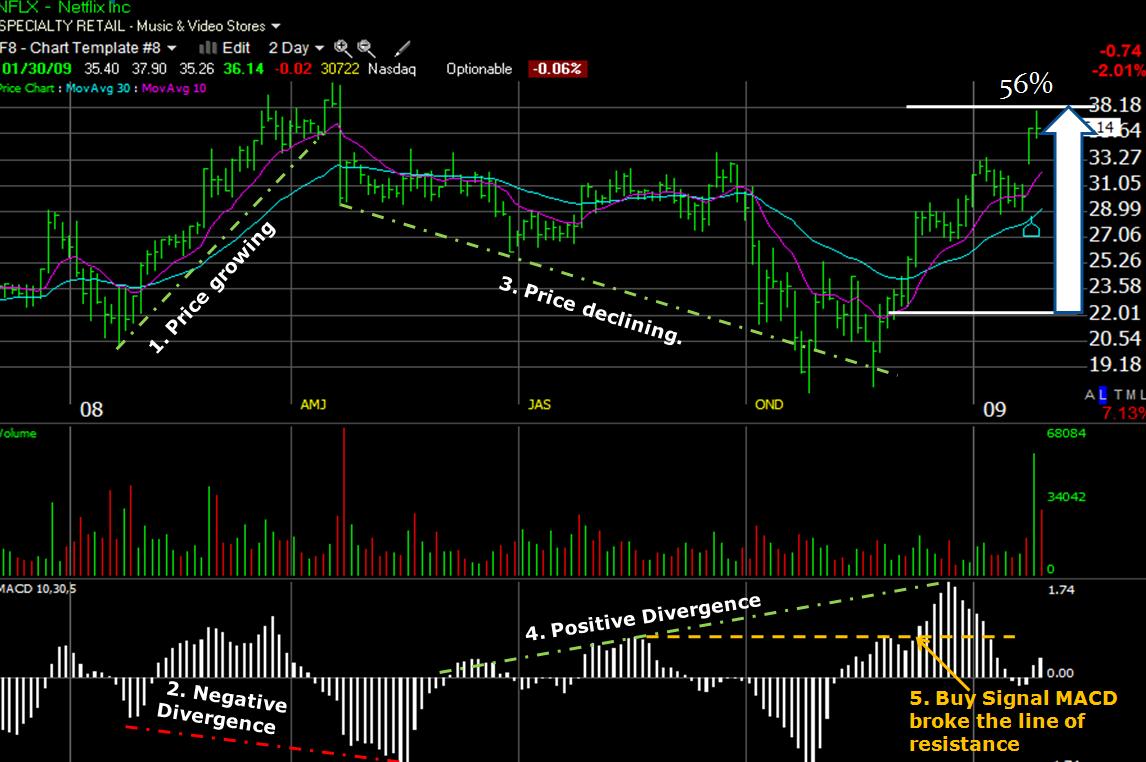
TC2000 chart courtesy of Worden Brothers, Inc.
Step 1 – Price Growing
The stock price is in growth mode, almost doubling in the first quarter.
Step 2 – Negative Divergence
The trick with MACD is to look at the trend; it is a powerful indicator when comparing the direction of the MACD Mountains with the Price Movement.
Point 2 illustrates that although the price doubled in 2008, we saw the MACD make lower lows “negative divergence.”
We see a change in the MACD from positive to negative, and the large mountain (below the Zero Line) forms. ACD is an oscillating indicator and, as such, is always tied to the Zero line in the middle.
Step 3 – Price declining
Here we see a strong decline in price for the rest of 2008 until November. Using a trendline to show this helps us visualize the direction easier.
Step 4 – Positive Divergence
Simultaneously, the price is declining; we see a longer-term Positive Divergence occurring from June to December. This essentially means that the “Gas in the tank of the sellers is slowly reducing.”
However, we should not have waited until December to buy the stock. That would have been way too late. Instead, we would look to Point 5.
Step 5 – Buy Signal
MACD broke through the resistance line: we see the MACD breaking strongly past its previous high. I plotted a trendline in orange to show this clearly.
If you had used MACD as your BUY SIGNAL, you would have netted 56% in 4 months.
Please do not think I searched through hundreds of charts to find a good example to demonstrate here. This was a stock on my watchlist and indeed bought based on this lesson.
Fibonacci Stock Chart Indicator
Many ardent investors follow the Fibonacci principles almost religiously across the globe. Indeed, when you look at applying these scientific observations, you may be compelled to take them seriously.
We will use Fibonacci Retracement for this analysis example and apply it to the 2007 to 2008 Financial Crisis. We will look at the charts a few years later, in 2011.
What are Fibonacci Numbers In the Stock Market?
Fibonacci numbers are revered in mathematics as the numbers that describe the natural world. The sequence is simply the sum of any two numbers equals the next in the sequence.
1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34,55,89 etc…..
1+1=2
1+2=3
2+3=5
The theory behind Fibonacci is that this mathematical pattern can be used to predict the waves of a trend. The most important numbers seem to be in percentage terms 38, 50, 62.
Therefore, if a trend moves from $1 to 100$, it may retrace (go back down) to 1 of 3 important levels: $ 62, $50, or $38.
Applying Fibonacci on a Chart
This is a long-term weekly chart of the S&P500; it stretches back five years, from 2007 to 2011. This enables us to get some perspective on the Financial Crisis in 2007 and compare that to what happened later.
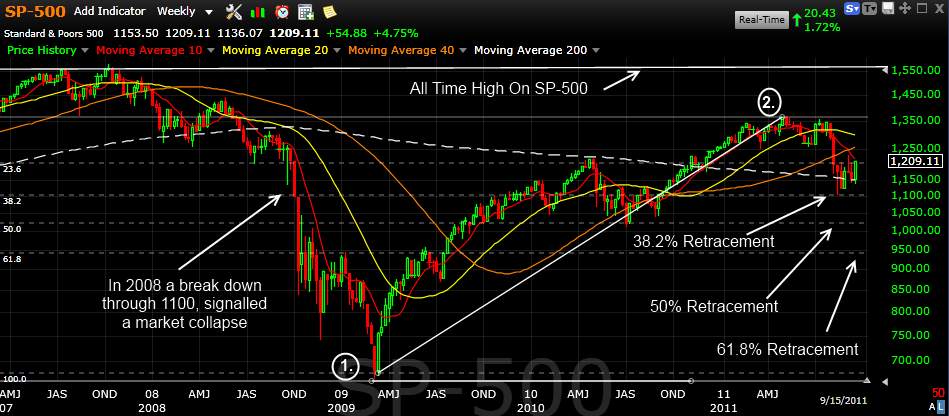
You can use Fibonacci Retracement on any chart by following these instructions.
- Select the Fibonacci Retracement Tool in your charting package
- Select the Lowest Point on the chart; in this case, Point 1
- Drag your mouse to the highest point on the chart in the future; in this case, Point 2
You should then see the important Retracement levels are drawn (the Grey Dotted Lines)
Important Points to Note
- In the 4.5 years since October 2007, the market has failed to reach an all-time high of 1,550.
2. In 2008, when the market broke down by 1,100 points, the market collapsed.
The Market Moves Down
- The retracement line at 38.2% equals 1,125 points in the index. This is currently a support line.
- Any drop through this area could see a further drop to 1,000 points, the 50% retracement line.
- The next drop zone could be 950 points, the 61.8% retracement line. This maps back to 2009 /2009 perfectly.
The Market Moves Up
We can see that the 21.6% retracement line at circa 1,225 provides resistance. A strong move up through this area would be positive.
7. Estimate the Future Direction of the Stock Price
Using Trendlines to make Buy and Sell Decisions
So we have seen the Sideways Channel and the W bottom. But how do we know when a stock is going to take off?
The truth is we never really know.
All we can do is make judgments based on what we see. Do not forget we are only buying Stocks of companies that have
- Excellent Earnings per Share
- Strong acceleration in the growth of Earning per Share
- Excellent Revenue growth
So we are, in essence, giving ourselves a great head start and reducing our overall risk.
4-Step Guide to Using Trendlines for Buy & Sell Decisions
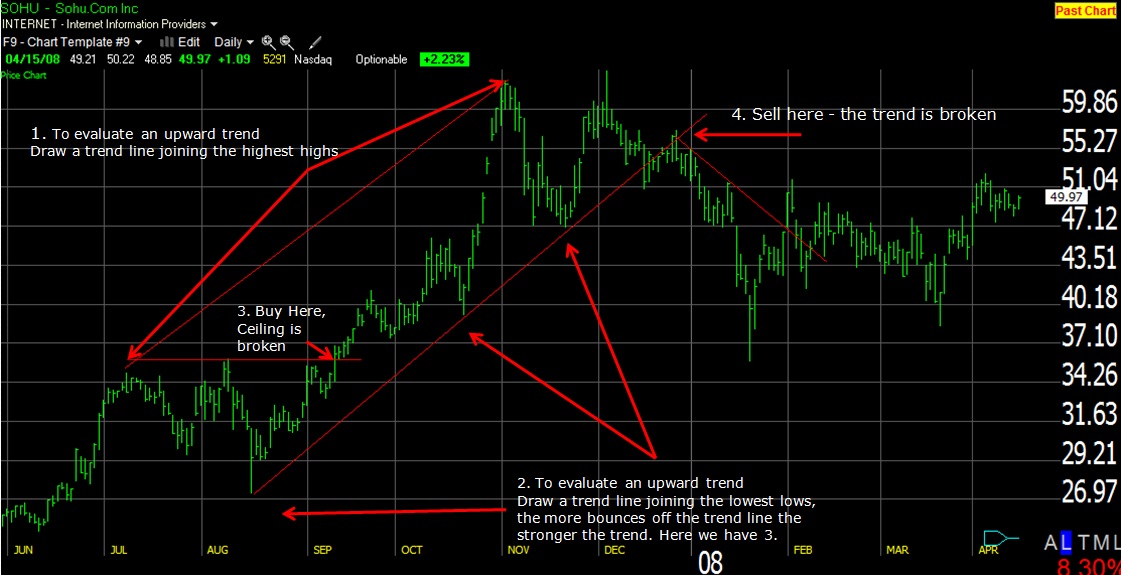
4 Steps to Draw the Trendlines on the Chart
- To evaluate an upward trend, draw a line joining the highest highs
- For the floor of the uptrend, draw a line connecting the lowest lows. The price here bounces 3 times off the bottom trendline but proceeds higher. The more bounces off a trendline, the stronger the trend.
- A trendline shows that the price has moved strongly past the previous high; this is a BUY Signal at $35.50.
- Finally, the price is exhausted and falls through the bottom resistance line at $53.
Buying and selling based on the trendlines here would have netted you a tasty 49%.
Life is never that easy, and showing this in retrospect does mean we benefit from hindsight. This is why Wall St.’s finest minds have a whole host of other technical indicators that accompany price to enable you to assess trend quality.
Summary: How to Read Stock Charts For Beginners
You can learn how to read stock carts by learning 7 process steps; open a chart, select a chart type, choose a timeframe, draw trendlines, add indicators, and estimate future price direction.
You know how to read stock charts and understand volume and stock chart indicators. But what is next? Take your skills to the next level with our 5 Star Amazon Rated Liberated Stock Trader Pro Stock Market Training Course
eBook PDF Download
You can download the PDF eBook here
Are You Looking For Stock Investing & Trading Software? Here Are My Favorites.
My favorite software for trading is TradingView because it does everything well. It has backtesting, great charts, stock screening, and an active community of over 3 million people sharing ideas, plus a free plan available globally.
My favorite software for investing is Stock Rover, as it specializes in deep fundamental financial screening, research, and portfolio management. It is the ideal platform for dividend, value, and growth investing.
My favorite software for stock market news is Benzinga Pro, with its super-fast real-time news engine, squawk box, and news impact ratings.
My favorite AI trading software is TrendSpider which enables automatic pattern recognition for Trendlines, Candlesticks, and Fibonacci levels. Trade Ideas uses AI to generate high probability daily trading signals for auto-trading.
My favorite stock-picking service is Motley Fool Stock Advisor, which has a proven track record of beating the market with excellent stock research reports.
Read the Full Top 10 Stock Market Software Testing & Review
Source link
#Read #Stock #Charts #Boss #Beginners #Guide #pdf